Dart class-based programming language
Dart is a new class-based programming language for creating structured web applications. Developed with the goals of simplicity, efficiency, and scalability, the Dart language combines powerful new language features with familiar language constructs into a clear, readable syntax.
Key features
Key features of the Dart language include:
Classes
Classes and interfaces provide a well understood mechanism for efficiently defining APIs. These constructs enable encapsulation and reuse of methods and data.
Optional types
Dart programmers can optionally add static types to their code. Depending on programmer preference and stage of application development, the code can migrate from a simple, untyped experimental prototype to a complex, modular application with typing. Because types state programmer intent, less documentation is required to explain what is happening in the code, and type-checking tools can be used for debugging.
Libraries
Developers can create and use libraries that are guaranteed not to change during runtime. Independently developed pieces of code can therefore rely on shared libraries.
Tooling
Dart will include a rich set of execution environments, libraries, and development tools built to support the language. These tools will enable productive and dynamic development, including edit-and-continue debugging and beyond—up to a style where you program an application outline, run it, and fill in the blanks as you run.
Design goals
The Dart programming language is presented here in its early stages. The following design goals will guide the continued evolution and refinement of this open source project:
Create a structured yet flexible programming language for the web.
Make Dart feel familiar and natural to programmers and thus easy to learn.
Ensure that all Dart language constructs allow high performance and fast application startup.
Make Dart appropriate for the full range of devices on the web—including phones, tablets, laptops, and servers.
Provide tools that make Dart run fast across all major modern browsers.
These design goals address the following problems currently facing web developers:
Small scripts often evolve into large web applications with no apparent structure—they’re hard to debug and difficult to maintain. In addition, these monolithic apps can’t be split up so that different teams can work on them independently. It’s difficult to be productive when a web application gets large.
Scripting languages are popular because their lightweight nature makes it easy to write code quickly. Generally, the contracts with other parts of an application are conveyed in comments rather than in the language structure itself. As a result, it’s difficult for someone other than the author to read and maintain a particular piece of code.
With existing languages, the developer is forced to make a choice between static and dynamic languages. Traditional static languages require heavyweight toolchains and a coding style that can feel inflexible and overly constrained.
Developers have not been able to create homogeneous systems that encompass both client and server, except for a few cases such as Node.js and Google Web Toolkit (GWT).
Different languages and formats entail context switches that are cumbersome and add complexity to the coding process.
Show me the code
Here are several code snippets to give you a feel for what Dart code looks like.
Classes and interfaces
Dart’s interfaces and classes provide you with a set of reusable and extensible building blocks. An interface defines a basic set of methods and constants, sometimes by inheriting from other interfaces. A class can implement multiple interfaces, but it only inherits from a single superclass.
The following example defines an interface, along with a class and subclass that implement it:
interface Shape {
num perimeter();
}
class Rectangle implements Shape {
final num height, width;
Rectangle(num this.height, num this.width); // Compact constructor syntax.
num perimeter() => 2*height + 2*width; // Short function syntax.
}
class Square extends Rectangle {
Square(num size) : super(size, size);
}
Optional types
Dart provides, at the programmer’s option, a mixture of static and dynamic checking. When experimenting, the programmer can write untyped code for simple prototyping. As the application becomes larger and more stable, types can be added to aid debugging and impose structure where desired.
For example, here is a sample of untyped code in Dart that creates a new Point class that has parameters x and y and two methods: scale() and distance().
#import(‘dart:math’);
class Point {
var x, y;
Point(this.x, this.y);
scale(factor) => new Point(x*factor, y*factor);
distance() => sqrt(x*x + y*y);
}
main() {
var a = new Point(2,3).scale(10);
print(a.distance());
}
Here is what this code looks like with types added that ensure that x, y, and factor are of type num, and that a Point contains two values of type num:
#import(‘dart:math’);
class Point {
num x, y;
Point(num this.x, num this.y);
Point scale(num factor) => new Point(x*factor, y*factor);
num distance() => sqrt(x*x + y*y);
}
void main() {
Point a = new Point(2,3).scale(10);
print(a.distance());
}
How can I use Dart?
You can run Dart code in several ways:
Compile Dart code to JavaScript that can run in any modern browser:
Chrome, Safari 5+, and Firefox 4+ (more browser support coming shortly)
Execute Dart code directly in a VM on your computer
With a new MIME type, use Dart in a browser without first compiling to JavaScript
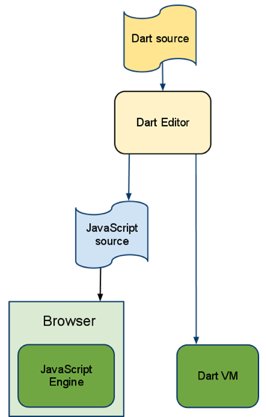
Dart Editor
Dart Editor is a tool for creating, modifying, and launching Dart web apps. With one click, you can compile a Dart web app to JavaScript and launch the app in a browser. Taking advantage of Dart’s structured nature, Dart Editor supports method name completion and refactoring.
For information about downloading and using Dart Editor, see the Dart Editor tutorial.
New MIME type
You will be able to link to a Dart program directly from an HTML page. Here is the proposed new MIME type, “application/dart”:
< !DOCTYPE html>
Simple Dart Web App
dart is starting up…
The dart.js file above will swap out the application/dart tag with a text/javascript tag if the browser does not have an embedded Dart virtual machine.
The following is the Dart code for the page above:
#import(‘dart:html’);
class SimpleDartWebApp {
void run() {
write(“Hello World!”);
}
void write(String message) {
// the HTML library defines a global “document” variable
document.query(‘#status’).innerHTML = message;
}
}
void main() {
new SimpleDartWebApp().run();
}
Tools
The Dart language is accompanied by a set of tools to aid rapid prototyping, coding, and debugging for the entire development cycle. Offerings include:
The Dart Editor
The dart2js compiler
The Dart VM
Dartium: Chromium with an embedded Dart VM
On the client side, you can deploy Dart apps in two ways. For browsers without an embedded Dart VM, you can compile the Dart code to JavaScript, using the dart2js compiler. This compiler generates ECMAScript5-compatible JavaScript from the Dart code. Dart code can run directly in browsers that have a Dart VM, including Dartium (a special build of Chromium) and eventually Chrome.
On the server side, the Dart code runs directly on the command line, for fast iteration and for cloud-based tasks.
Libraries
Dart provides the following libraries to support web and web server development:
Core Library
Contains interfaces to support common data structures and operations.
HTML Library
Contains interfaces to the HTML5 DOM, loosely based on the proposed HTML5 standard as specified by the W3C/WHATWG. These interfaces will evolve in parallel with the HTML5 standards.
I/O Library
Contains interfaces to read and write files, open directories, open network sockets, and run HTTP servers. This library is for command-line Dart programs.
Isolate Library
Contains interfaces for spawning and communicating with isolates, the mechanism for concurrency and security in a Dart program.
Crypto Library
Contains interfaces for creating one-way hashes (SHA1, MD5, SHA256) and HMAC support.
JSON Library
Contains the ability to parse and produce JSON-encoded text.
Unit Test Library
Contains functions and classes for writing unit tests in Dart.
More About Dart class-based programming language
http://www.dartlang.org/docs/technical-overview
Download dart Editor
http://www.dartlang.org/downloads.html
Why did Google create Dart?,Does the web really need,another language?,Show me the code,How can I play with Dart?,How about a real editor?,What’s new about Dart?,Why does Dart look so familiar?,What is in the Dart platform?,Should I use Dart for my app today?,How do you expect people to use Dart?,How can I compile to JavaScript?,What libraries are available?,Show me more code,Where can I learn more?,learn more about Dart,play with Dart in your browser,dart Structured web apps,Generics in Dart,Optional Types in Dart,idiomatic Dart,dart game,dart rules,dart board,dart google language,dart doubleclick,dart google,dart wiki,dart tag,google dart programming language,google dart download,google dart examples,google dart jquery,google dart vs javascript,google dart showcase,google dart news,google dart cookie,what is google dart